Gluten Intolerance

Gluten contains two main proteins called glutenin and gliadin. Gliadin is responsible for the majority of the negative health effects within humans however, similar proteins such as hordein in barley, secalin in rye and avenin in oats are known to cause issues.
When flour is mixed with water, gluten proteins form a sticky glue-like consistency. Which makes the dough elastic and gives bread the ability to rise when baked. Gluten can be found in many modern food products including bread, pasta, cake & biscuits/cookies, crackers, breakfast cereals and pastries. It can also be found in lager, beer, ale and highly processed foods.
What is gluten intolerance?
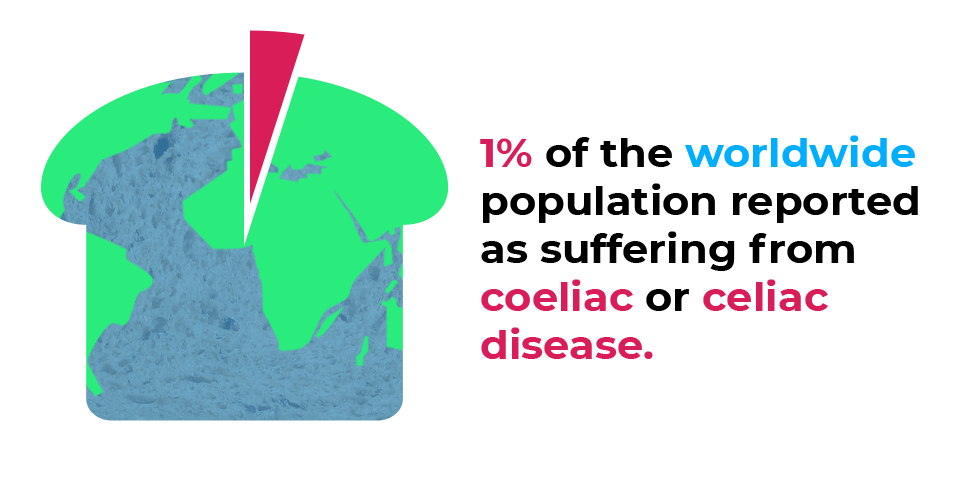
It has been estimated that between 0.5-13% of the population suffer from this condition with symptoms including stomach pain, tiredness and bloating.
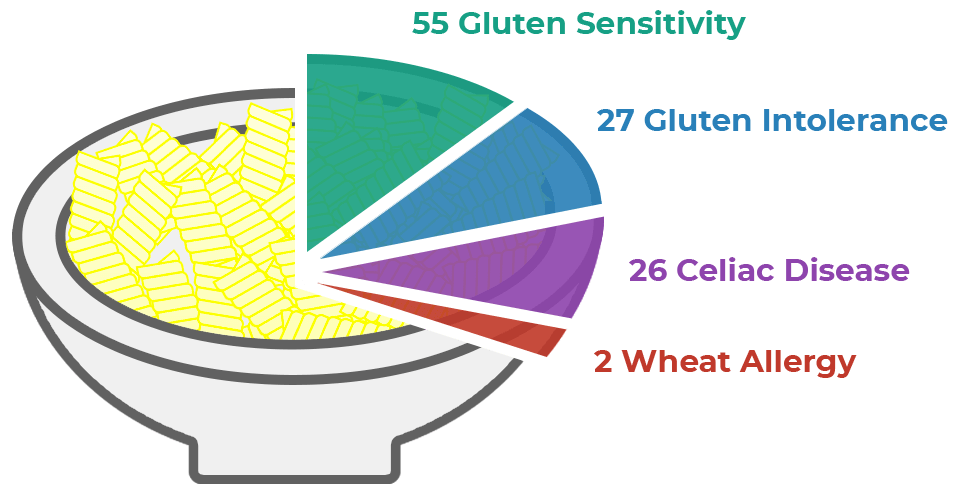
A study published in 2015 reviewed nearly 400 people with self-diagnosed gluten intolerance or sensitivity and investigated whether a gluten-free diet improved their symptoms.
Results showed that 26 people had celiac disease and 2 had an allergy to wheat. From the remaining people, 27 of the 364 were diagnosed as gluten-sensitive/intolerant.
Only 55 people of the sample (14.5%) had a detectable issue with gluten and others were due to other causes or trigger items.
Wheat allergy

Coeliac disease
The immune system attacks the gluten as a foreign invader and also damages the lining of the gut.
The damages to the gut wall can cause nutrient deficiencies, severe digestive issues and an increased risk of other health issues.
Celiac disease can be difficult to diagnose and should be referred to a medical practitioner.
Gluten-Free diet
The first thing you need to do is start reading the labels on everything you eat.
You’ll soon realize that gluten, especially wheat, is added to a surprising number of foods.
You should also eat mainly whole, healthy foods, as most whole foods are naturally gluten-free. Avoid processed food, cereals and grains that contain gluten.
Gluten-free grains

Corn

Rice

Quinoa

Flax

Sorghum

Tapioca

Millet

Buckwheat

Arrowroot

Oats

Amaranth
Gluten-free foods
Examples of naturally gluten-free foods include:
Meats

Fish

Eggs

Dairy

Fruits

Vegetables

Legumes

Nuts
Tubers
Gluten free alternatives to traditional foods
How, then, do you go about embracing these alternatives?
Removing gluten from your diet
Gluten substitutes: how to maintain your nutrition
Below are good examples of nutritional alternatives when eliminating gluten-containing grains:
B Vitamins
Vitamin E
Almonds, Apricots, Avocado, Blackberries, Broccoli, Collards, Crayfish, Guava
Hazelnuts, Herring, Kale, Kiwi, Mango, Nectarines, Olive Oil, Peach
Pistachios, Prawn/shrimp, Raspberries, Salmon, Smoked Salmon, Spinach, Squashes, Sunflower Oil, Sunflowers Seeds, Swiss Chard, Swordfish, Trout, Turnip Greens, Yams
Calcium
Almonds, Broccoli, Kale, Low-fat Cheddar, Low-fat Mozzarella, Pak Choi, Sugar Snap Peas, Tofu, Watercress, Yogurt
Magnesium
Almonds, Apricots, Avocado, Brazil Nuts, Broccoli, Buckwheat Millet Brown Rice Quinoa, Cashews, Coconut, Collards, Corn, Dates, Figs, Grains, Kale, Kelp, Peanuts, Prawns, Soya Beans, Spinach, Swiss Chard, Tofu, Turnip Greens, Walnuts
Manganese
Aduki Beans, Blueberries, Chickpeas, Grains, Hazelnuts, Kale, Lentils, Lima Beans, Mussels, Oats (Gluten-free) Brown Rice Quinoa, Pecans, Pine Nuts, Pineapple, Pumpkin Seeds, Raspberries, Sesame Seeds, Soybeans, Spinach, Strawberries, Sunflower Seeds, Tofu, Yams
Zinc
Beef, Cashew Nuts, Chicken, Chickpeas, Cocoa Powder, Dark Chocolate, Grains, Lamb, Mushrooms, Oats (Gluten-free), Pork, Pumpkin Seeds, Sesame Seeds, Spinach, Sunflower Seeds
Iron
Almonds, Beef, Cashews, Chicken Liver, Chickpeas, Clams, Dark Chocolate, Grains, Hazelnuts, Kale, Kidney Beans, Lamb, Lentils, Lima Beans, Mussels, Oats (Gluten-free), Oysters, Peanuts, Pine Nuts, Pumpkin Seeds, Sesame Seeds, Soybeans, Spinach, Sunflower Seeds, Swiss Chard, White Beans
Selenium
Beef, Brazil Nuts, Brown Rice, Cottage Cheese, Eggs, Grains, Liver, Mushrooms, Oysters, Sardines, Shrimp, Sunflower Seeds, Tuna, Turkey
Copper
Cashews, Collard Greens, Dark Chocolate, Garbanzo Beans, Grains, Kale, Lentils, Lima Beans, Liver, Mushrooms, Oats, Sesame Seeds, Soybeans, Spinach, Spirulina, Sunflower Seeds, Swiss Chard, Tempeh, Walnuts
Phosphorus
Almonds, Brazil Nuts, Cashews, Chicken, Cottage Cheese, Crab, Grains, Liver, Mackerel, Milk, Oats (Brown Rice Quinoa), Pine Nuts, Pistachios, Pork, Pumpkin Seeds, Salmon, Sardines, Scallops, Sunflower Seeds, Turkey, Yogurt
Our Best Selling Tests
Our most popular tests. Our non-invasive bioresonance sensitivity test uses a small hair sample to test 1400 Foods, inhalants, vitamins and minerals.
- Budget

Core Sensitivity Test
Was £69.00 Now £27.00 Save £42.00
400 item food, environmental and metals sensitivity test.

Premium Sensitivity Test
Was £89.00 Now £35.00 Save £54.00
970+ item comprehensive sensitivity and health test report.
- ADVANCED

Advanced Sensitivity Test
Was £99.00 Now £47.00 Save £52.00
1400 items, our most advanced sensitivity and health test.
